Types of RAID Arrays: A Simple Explanation of Features, Advantages, and Disadvantages
- Published: August 2, 2022
- Updated: August 3, 2022
There are the following levels of RAID: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Moreover, there are some combinations: 01, 10, 50, 60 and others. Different types of RAIDs solve different problems; here we will focus on some of the most common types of RAIDs. We offer you to delve into the working principles of RAID and consider the advantages and disadvantages of the main types of RAIDs, so that you will be able to make the right choice for your goals.

Table of Contents
- RAID 0 (striping)
- RAID 1 (mirroring)
- RAID 5 (striping with distributed parity)
- RAID 6 (striping with double parity)
- JBOD
- RAID 01 or RAID 0+1
- RAID 10 or RAID 1+0
- RAID + Spare
- Comparative characteristics of different types of RAID
- What should you do if the array failed and all data was lost?
- How to use Magic RAID Recovery software to recover files from RAID?
RAID 0 (striping)
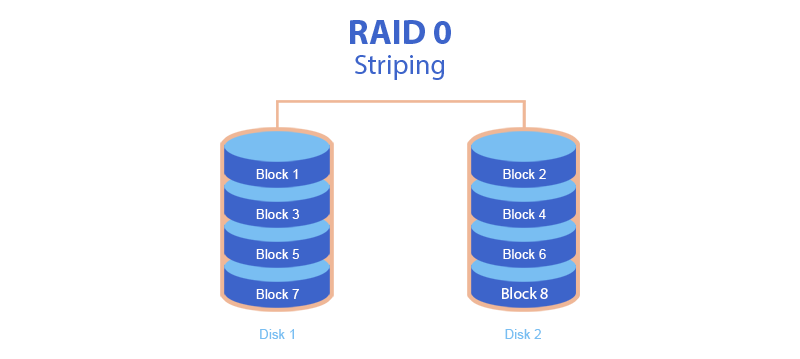
RAID 0, also known as a striped set or striped volume, represents an insecure RAID system. This means that if one of the hard disks fails, the data will be lost. Let’s learn some of the main features of RAID 0:
- Minimum 2 hard disks are required to create RAID 0.
- When creating a RAID system, it is necessary to determine the “block size”. Using this parameter, the data is divided according to the block size and written to each hard disk by turn. Globally speaking, the first 64kb of the file are written to the first HDD, the next 64kb are written to the second HDD, and so on.
- This system allows you to write or read portion of the data on each disk simultaneously. Thus, the reading and writing speed increases on RAID 0.
Advantages of RAID 0
- The highest reading and writing speed
- 100% efficient use of disk space.
The disadvantage of RAID 0
The lowest data security. However, if one hard disk fails, then the entire RAID 0 will be unable to function. Indeed, the files are partitioned and re-partitioned on all the hard disks, so all the hard disks are necessary to get all the parts of the file.
Causes of RAID 0 failures
- Physical problem on one of the hard disks.
- Loss of RAID configuration.
- RAID reconfiguration.
- SMART error on one of the hard disks.
RAID 1 (mirroring)
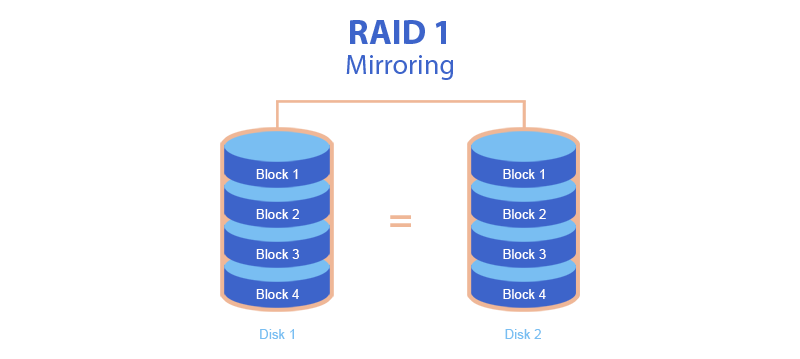
RAID 1, known as mirroring RAID or simply mirroring, is a secure RAID system. So far at least one of the hard disks is fault free, this RAID system will work. Here is a list of features of RAID 1:
- Minimum 2 hard disks are required to create RAID 1.
- The data is simply duplicated to each hard disk of RAID 1. Such a RAID system is very secure, but does not work fast when reading/writing. Indeed, the system is designed so that the data must be duplicated to all the hard disks of the array every time.
Advantages of RAID 1
- Rather high degree of reliability.
- The highest reading speed due to parallel requests to all disks at once.
The disadvantage of RAID 1
Since each subsequent hard disk is a clone of the first one, as a result you will have only half of their total memory.
Causes of RAID 1 failures
- Loss of RAID configuration.
- Reconfiguration of RAID 1 to another RAID type.
- Power line failure.

RAID 5 (striping with distributed parity)
RAID 5, known as block-level striping with distributed parity, is a pretty secure RAID system. It can work in case of failure of one disk in RAID. If more than one disk fails, the RAID system will stop working. Let’s consider the features of the principle of RAID 5 operation:
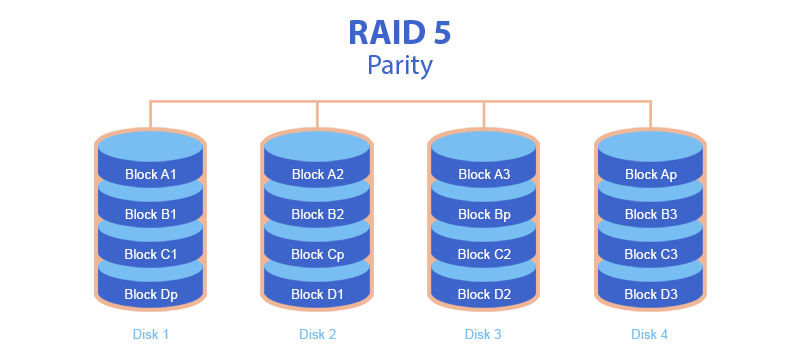
- Minimum 3 hard disks are required to create RAID 5. When calculating parity, RAID 5 can work if one of the hard disks fails.
- Let us assume that we have RAID 5 consisting of 4 hard disks. The file written in the RAID system is divided into small blocks of X sectors in length. The first block of the file is written to the first HDD, the second to the second HDD and the third to the third HDD. Then parity is calculated from these 3 blocks (this is the result of XOR for 3 blocks). This parity is written on the fourth HDD. This goes on and on for each row.
- To avoid the presence of all the parity on one hard disk, the parity is written to another hard disk in a cyclic manner. This is called the parity offset type.
- Parity is XOR (exclusive OR) calculated for data blocks. If one of the hard disks fails, there is no data block in this line. The missing block is calculated from the remaining blocks by a simple equation.
- When replacing a failed hard disk, the missing data is recreated thanks to other RAID 5 hard disks.
Advantages of RAID 5
- Significant increase in reading speed compared to disks that are not combined into RAID.
- High efficiency of disk space usage in comparison with RAID 1, 6, 10high efficiency of disk space usage in comparison with RAID 1, 6, 10.
- Basic level of reliability (only one of the disks in the array is allowed to fail).
The disadvantage of RAID 5
A significant disadvantage of RAID 5 is that when one of the disks fails, the entire array goes into critical mode, all writing and reading operations are accompanied by additional manipulations and load, performance drops sharply, disks begin to warm up. If you do not take urgent measures, you can lose all your data.
Causes of RAID 5 failures
- Loss of RAID configuration.
- Failure of two or more hard disks.
- Incorrect RAID reconfiguration.
RAID 6 (striping with double parity)
RAID 6, known as block-level striping with two distributed parity blocks, is a pretty secure RAID system. Even if two hard drives in the array fail, the data is still safe. Let’s consider the features of RAID 6.
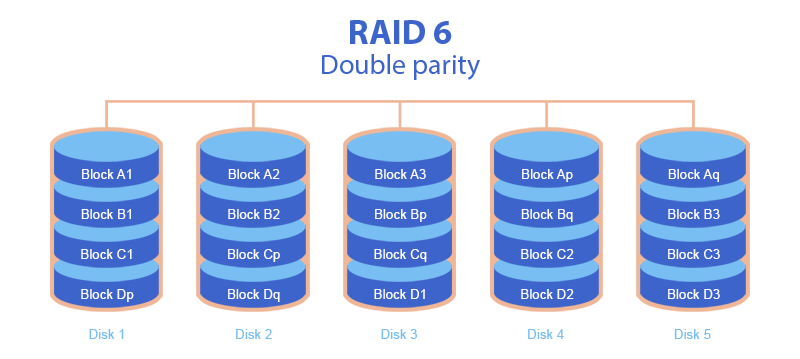
- Minimum 4 hard disks are required to create RAID 6. Thanks to two different parity, this RAID system can withstand the loss of 2 disks.
- Let us suppose that we have 5 RAID 6 hard disks. The data is divided into blocks of X sectors. The first block is written to the first HDD, the second block to the second HDD, the third block to the third HDD. As soon as these 3 blocks are written to 3 hard disks, the first parity calculation is performed according to these three blocks. This parity is written on the fourth HDD. Then the second parity is calculated by another method and written to the fifth HDD. Once these two parity values are saved, the following data blocks are written according to the same process. At the same time, the first parity is calculated as in RAID 5 (normal XOR), and the second one is calculated using a more complex formula (based on Reed-Solomon codes).
- To avoid the presence of all the parity values on the same hard disks, the parity values are written to different hard disks in a cyclic manner each time.
- The loss of 2 hard drives (i.e., 2 data blocks per line) can be recalculated due to double parity. When replacing a faulty hard disk, the missing data is automatically restored by using other RAID 6 hard disks.
Advantages of RAID 6
- Fast RAID array reconstruction.
- Reliability does not decrease with increasing size of array.
- Maximum possible capacity for installed disks and data channel.
The disadvantage of RAID 6
Complex implementation, too many resources are necessary to calculate two checksums at once. Compared to RAID 10 and RAID 5, RAID 6 technology represents the RAID level with the lowest capacity and the highest hardware requirements.
Causes of RAID 6 failures
- Loss of RAID configuration.
- Failure of three or more hard disks.
- Incorrect RAID configuration.
JBOD
JBOD (abbr. for Just a bunch of disks) is several disks combined into one large volume or disk array. The features of JBOD include:
- Files are written to the first HDD until it is full, then to the second, and so on.
- If one of the hard drives fails, all data on that hard drive will be lost. Data storage security is at a low level. However, JBOD is less dangerous than RAID 0.
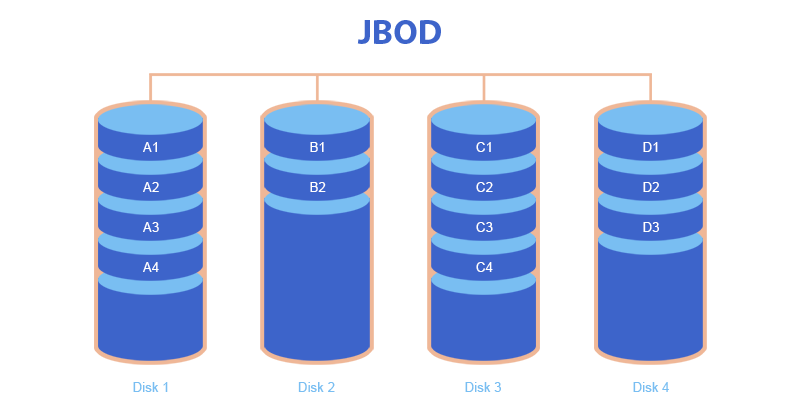
Advantages of JBOD
- The capacity of the array is equal to the total volume of its constituent disks and it can be easily expanded with the help of additional drives. The load on the processor when working with JBOD is comparable to the load when working with a single disk, i.e. very small.
- When one of the disks of the JBOD array fails, only the data that was stored on it is lost.
- There is no loss of disk space when organizing JBOD.
- JBOD is applied most often when the user needs to take hold of the total capacity of all drives in the array, i.e. itmain advantage is capacity increase.
The disadvantage of JBOD
High cost is a significant downside. And there are no other significant advantages from this method of combining hard disks, besides increasing the capacity. Also, unlike RAID 0, the speed of the array does not increase.
Causes of JBOD failures
- Failure of any HDD.
- Loss of JBOD configuration.
- Incorrect configuration of the JBOD array.
RAID 01 or RAID 0+1
RAID 01 is a combination of two RAID systems (RAID 0 and RAID 1) into an array. So RAID 01 is an array within an array. Let’s find out the features of RAID 01:
- This system provides secure storage thanks to RAID 1, as well as faster reading and writing thanks to RAID 0.
- This is less reliable than RAID 10, because if the hard disk fails, it will cause the entire pair to fail.
- In RAID 01, data is divided into blocks of X sectors. The first block is written to the first hard disk of the pair, the second block is written to the second hard disk of the same pair, etc. (the pair is RAID 0). Then this pair is cloned to another pair (two pairs as a mirror, this is RAID 1). This system offers reliability and good speed.
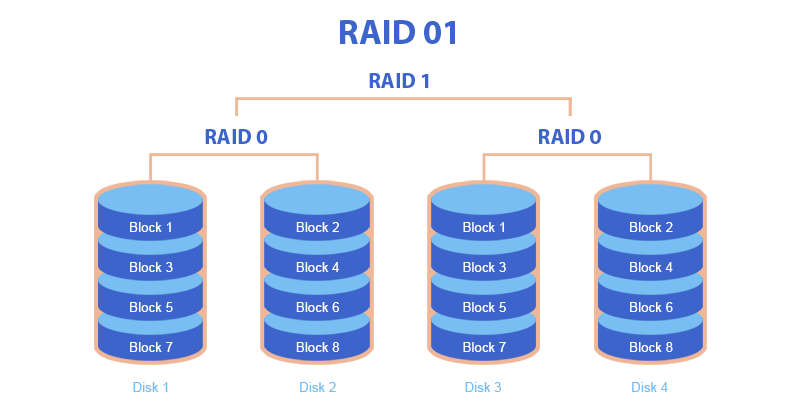
Causes of RAID 01 failures
- Loss of RAID configuration.
- Failure of all hard drives of one pair.
- Incorrect configuration of RAID.
RAID 10 or RAID 1+0
RAID 10 is a combination of two RAID systems (RAID 1 and RAID 0). Just like RAID 01, RAID 10 is an array within an array. Let’s consider the key features of RAID 10.
- This system provides secure data storage thanks to RAID 1, as well as faster reading and writing thanks to RAID 0.
- The technology of RAID 10 is quite reliable, since data can only be lost if two hard disks of the same pair (RAID 1) fail at the same time.
- In RAID 10, data is divided into blocks of X sectors. The first block is written to two HDDs (RAID 1, mirroring), and the second to two other HDDs (another RAID 1). This system offers reliability and good speed.
- RAID 10 is more secure than RAID 01.
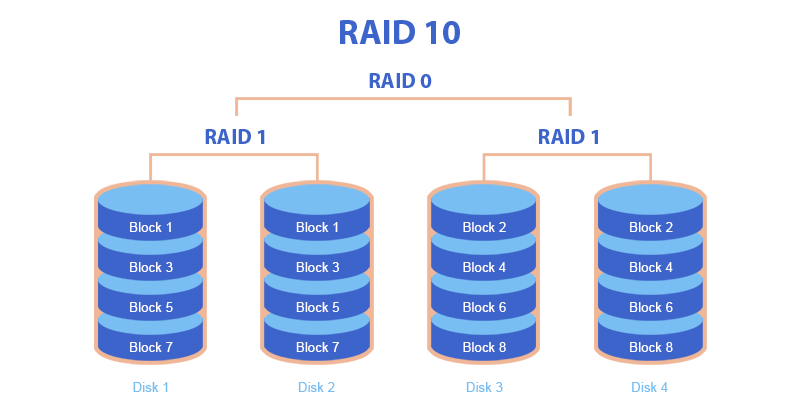
Causes of RAID 10 failures
- Loss of RAID configuration.
- Failure of all hard disks of the same branch.
- Incorrect RAID configuration.
RAID + Spare
These are RAID systems with a spare HDD, which are more resistant to HDD failures. And the peculiarity of the RAID + Spare system is that if we have RAID 5 with a faulty hard disk, another hard disk failure is unacceptable, otherwise data will be lost. But if there is a spare disk, it will immediately replace the faulty HDD.
The missing data is restored to the backup disk, and as soon as this process is completed, the RAID system is no longer in the state of failure. Thus, the spare hard disk is used only in case of failure of one of the disks of the array.
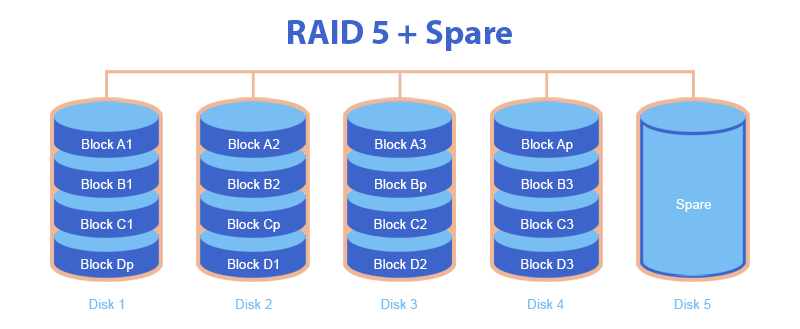
Only the following RAID systems can work with a spare disk:
- RAID 1 + Spare
- RAID 5 + Spare
- RAID 6 + Spare
- RAID 10 + Spare
Comparative characteristics of different types of RAID
| Characteristics | RAID 0 | RAID 1 | RAID 5 | RAID 6 | RAID 01 | RAID 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum quantity of disks | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Maximum quantity of disks | 16 | 3 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Reading performance | High | Above average | High | High | Above average | Above average |
| Writing performance | Above average | Above average | Average | Average | Above average | Above average |
| Built-in backup disk | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Redundancy | – | + | + | + | + | + |
| Disk capacity usage | 100% | 50% | 67-94% | 50-88% | 50% | 50% |
What should you do if the array failed and all data was lost?
If the disks in the array have failed, the RAID controller has been broken, or the user has committed a number of erroneous actions during operation, there is a high probability of data loss. Regardless of the reasons, it is important to know the methods of lost files recovering.
Currently, there are various tools on the software market for data recovery from RAID. The simplest and most effective is Magic RAID Recovery. The intuitive and user-friendly interface of the program is available even for novice users. You don’t need to have any special technical skills to recover files using this utility.

How to use Magic RAID Recovery software to recover files from RAID?
1. Open the program and choose RAID for the analysis.
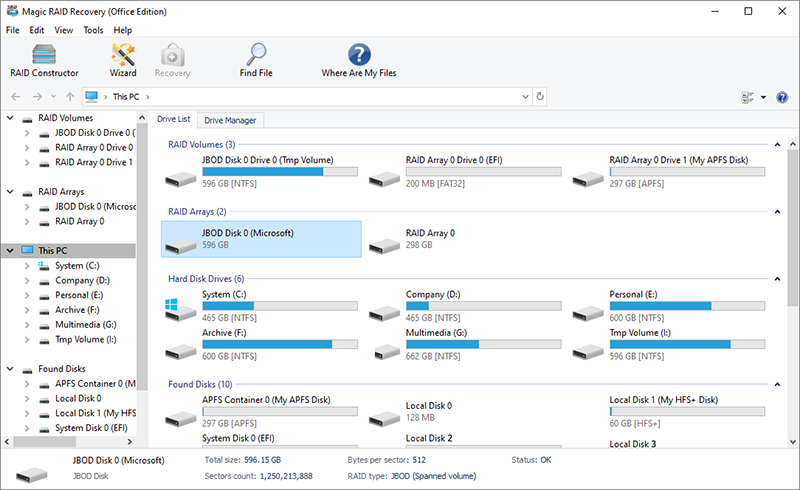
2. In addition to the automatically found RAID, you can create it manually with the necessary parameters.
3. Choose quick or full analysis and wait for the scan to finish. Restore necessary files or the entire RAID content.
4. Restore necessary files or the entire RAID content.
As you can see, the process of recovering deleted files from RAID is simple and easily understandable if you use the program Magic RAID Recovery. Try it right now to see first-hand how easy it is to recover data from RAID!
Like This Article?
FAQ
-
RAID 0 is the fastest RAID mode because data is written to all the disks of the volume. Moreover, the capacities of all disks are combined for optimal data storage. However, this array is not secure for data storage.
-
5 provides fault tolerance and improved read performance. At least three disks are required. However, the larger the number of disks is, the more efficient the use of disk space will be.
-
If your budget allows you, then RAID usage will give you many advantages. As we have already mentioned, RAID can improve storage performance and secure your valuable data.
Stay Tuned






Comments