Recovering Data from RAID 10: How to Restore Data from RAID 10
- Published: December 26, 2024
- Updated: January 8, 2025
In the age of digital technology and data storage, the reliability and security of information are paramount. One of the most popular solutions for enhancing data reliability is the use of RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations.

RAID 10, also known as RAID 1+0, combines the advantages of both RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping). However, even the most reliable RAID array can fail. In this article, we will take a detailed look at what RAID 10 is, how it works, and what steps to take to recover data from a RAID 10 array.
Table of Contents
What is RAID10?
RAID 10 is a configuration that combines mirroring (RAID 1) and striping (RAID 0) technologies. In this configuration, data is divided across multiple disks and mirrored, ensuring both high performance and reliability.
How Does RAID 10 Work?
RAID 10 requires a minimum of four hard disks. It first creates mirrors (i.e., copies) of the data on two disks and then divides these mirrors into two or more parts.
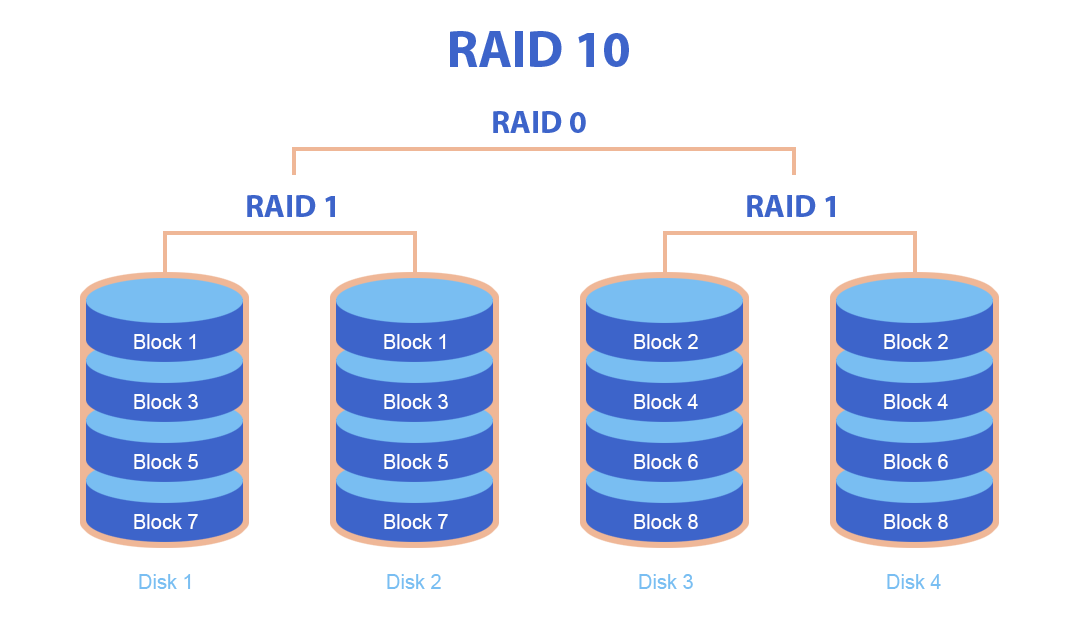
Structure of RAID 10:
- Mirroring: Data is written simultaneously to two disks. If one disk fails, the data can still be recovered from the mirror.
- Striping: Data is divided into blocks and distributed across multiple disks, providing faster access to information.
This structure gives RAID 10:
- High performance for read and write operations.
- High data protection in case of the failure of one or more disks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RAID 10
Like any technology, RAID 10 has its advantages and disadvantages. In this section, we will discuss what makes RAID 10 an ideal choice for many applications, as well as potential pitfalls that could affect its effectiveness and cost. Understanding these aspects will help you make an informed decision when choosing a RAID controller for your data storage needs.
Advantages of RAID 10:
- Resilience: RAID 10 can continue to operate even if multiple disks fail, as long as mirroring is not affected.
- High read and write speeds: Compared to other RAID configurations, RAID 10 offers excellent performance.
- Reliability: Data protection thanks to information duplication.
Disadvantages of RAID 10:
- High storage costs: Implementing RAID 10 requires at least twice as many disks as are actually needed for data storage. Thus, effective space utilization may be limited.
- Complex recovery: In the event of multiple disk failures, data recovery can become complicated.
Signs of RAID 10 Failure:
There are several signs that may indicate problems with a RAID array. These include:
- Performance issues: A decrease in read or write speed on the array may indicate a fault.
- Access errors: If you cannot access data or see error messages, this signals a potential failure.
- Emergency shutdowns: Damaged data blocks can lead to shut down or system crashes.
- Disk status indicators: Hardware RAID controllers usually have indicators to warn of disk failures.
If you notice one or more of these signs, it’s time to take action.
Steps to Recover Data from a RAID 10 Array
Recovering data from a RAID 10 array can be a critical task, especially when your files and information are essential for work or personal use. Despite its high reliability and performance, RAID 10 arrays are not immune to failures and data loss. However, don’t panic! This process can be successfully completed by following proven steps and recommendations. In this section, we will guide you through the process of recovering data from a RAID 10 array, starting from diagnosing issues and ending with regaining access to your valuable data. Our goal is to equip you with the necessary knowledge and tools for quick and effective data recovery in the event of system failure.
Step 1: Preparing for Recovery
Before beginning the recovery process, you should prepare:
- Stop using the array: If the RAID 10 array shows signs of deteriorating functionality, immediately cease operations to prevent further data damage.
- Back up the data: If possible, create backups of all accessible data before starting the recovery process.
- Identify hardware and software tools: Determine which tools and programs you will use for recovery. You may use both hardware and software solutions.
Step 2: Assessing the Array’s Condition
Before starting the recovery process, you need to analyze the system’s condition:
- Use monitoring utilities: Software tools, such as SMART, can help determine the status of the disks in the array. They provide information about potential issues with the disks.
- Check the RAID controller: If your array is managed by a hardware RAID controller, check its status using the software provided by the manufacturer. Many controllers have built-in diagnostic tools that can help identify problems like failures or loss of synchronization.
- Analyze logs: Review the system and RAID controller event logs. These logs can provide vital information about issues such as disk failures, error messages, or configuration problems.
Step 3: Troubleshooting
If you have identified a problem, you need to take steps to troubleshoot the issue. Here are a few actions you can take:
1. Replace the faulty disk: If you find that one or more disks in the RAID 10 array have failed, replace them with new ones. Typically, the RAID controller will automatically start the rebuilding process after replacing the disk.
2. Check connections: Ensure that all disks are properly connected. Sometimes connection problems can cause malfunctions in the array.
3. Restart the system: In some instances, a simple system restart can resolve temporary issues that caused the failure.
4. Reset the RAID configuration: If nothing else works, you may need to reset the RAID controller to factory settings and reconfigure the array. However, be cautious as this may lead to the loss of all data.
Step 4: Data Recovery
If troubleshooting did not help and the data is still inaccessible, proceed to the data recovery steps:
1. Use data recovery software: There are many data recovery programs that can help recover information from RAID 10. Some popular software includes:
- Magic RAID Recovery: Powerful data recovery software that repairs corrupted or deleted RAID arrays in fully automatic mode.
- R-Studio: Data recovery program that supports RAID arrays.
- EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard: An easy-to-use tool that supports data recovery from RAID.
- TestDisk: A free utility for recovering lost partitions and retrieving data from damaged disks.
2. Consult professionals: If the data recovery software fails to retrieve the data, you may need to seek assistance from professionals. Companies specializing in data recovery have specialized equipment and software for successfully recovering data from damaged or inaccessible RAID arrays.
3. Create disk images: Before using data recovery software, create disk images of each disk in the array. These images can be used to recover data without risking damage to the original disks.
Step 5: Completing the Recovery Process
After successfully recovering the data, take a few final steps:
1. Verify data integrity: Ensure that all recovered files are accessible and functional. Check them for damage.
2. Save recovered data: Create backups of all recovered data on another storage medium to avoid future loss.
3. Analyze the cause of the failure: Conduct an analysis to determine what led to the array’s failure. This can help prevent similar situations in the future.
4. Set up monitoring systems: Install monitoring tools to analyze the condition of your RAID array in real time. This can help you detect potential issues early on.
Preventing Problems with RAID 10
The best way to avoid issues with a RAID 10 array is through proper prevention. Here are some recommendations:
1. Regularly check disk health: Periodically check the status of all disks using SMART or other utilities.
2. Create backups: Always adhere to the golden rule of keeping data backups. RAID is not a substitute for backups but complements them well.
3. Monitor performance: Use monitoring software to track performance and system status, allowing you to receive alerts about potential issues.
4. Scheduled maintenance: Regularly conduct maintenance on your RAID array, including firmware updates for controllers, replacing aging or problematic disks, and testing all system components.
5. Logging operations: Keep logs of all operations with disks and RAID controllers. This can aid in analyzing problems and their causes in the future.
6. Employee training: If the RAID array is used in organizations, it is essential to train staff on the basics of data storage and methods for preventing and troubleshooting problems. This can help lead to quicker responses to emerging issues.
7. Choosing quality equipment: Use drives and RAID controllers from reputable manufacturers. Ensure that the hardware supports RAID 10 and has a strong reliability reputation.

Summarizing
Recovering data from RAID 10 can be a complex and multi-step process, but by following the outlined steps, you can significantly increase your chances of successful recovery. RAID 10 offers high performance and data storage reliability, but it requires careful management and monitoring.
Key Takeaways:
- Simple diagnostics and troubleshooting can help avoid total disk failures.
- Professional data recovery can be the solution in difficult situations when software tools cannot resolve the issue.
- Prevention is the best means to avoid potential data loss. Regular checks, backups, and monitoring can significantly reduce the risk of critical situations.
It’s important to remember that no system is immune to failure, and paying attention to the seamless operation of RAID 10 and data recovery processes will be beneficial for both home users and rely on reliable data storage.
What to Do If the Array Fails and All Data Is Lost?
If the disks in the array fail, the RAID controller breaks down, or the user makes a series of erroneous actions during work, there is a high likelihood of data loss. Regardless of the reasons, it’s essential to know the methods for recovering lost files.
Today, there are various software tools available on the market for recovering data from RAID arrays. One of the simplest and most effective options is Magic RAID Recovery. The user-friendly interface of the program is accessible even for beginners. You don’t need to possess specialized technical skills to recover files using this utility.
How to Use Magic RAID Recovery Software to Recover Files from RAID Array?
- Open the program and select the RAID array for analysis: The program will automatically detect the RAID configuration, or you can create it manually with the necessary parameters.
- Choose a quick or full scan: Select the scanning mode and wait for the process to complete.
- Recover the required files or all contents of the RAID array: After the scanning process, you will see the recoverable files, allowing you to choose what you’d like to restore.
As you can see, the process of recovering deleted files from a RAID array is simple and straightforward when using Magic RAID Recovery. Try it out now to experience firsthand how easy it can be to recover data from a RAID array!
Like This Article?
FAQ
-
The main signs of RAID 10 failure can include:
- Decreased performance: This manifests as slow write or read speeds of data.
- Error messages: Difficulty accessing data or loss of access to the array.
- Disconnection of individual hard drives: Typically indicated by LED indicators on the RAID controller or RAID management software.
- Critical error notifications: Alerts from the hardware RAID controller regarding faults.
-
In most cases, data can be recovered even if one or more disks in the array have failed, as RAID 10 maintains mirrored copies of data on additional drives. However, if the data on the failed drives is damaged or lost, the recovery will become more complex. In such cases, it’s advisable to seek assistance from professional data recovery services that have specialized equipment and expertise for extracting data from damaged arrays.
-
For successful data recovery from RAID 10, it is crucial to prepare adequately. Here are the key preparation steps:
- Stop using the array and disconnect power: This helps prevent further data damage.
- Check the condition of disks using monitoring software: Use tools such as SMART to assess the health of the disks.
- Create a disk image of each drive in the array before recovery attempts: This minimizes the risk of data loss.
- Consider using data recovery software or consult professionals: If you lack experience in recovery processes.
Stay Tuned






Comments