How to Create and Run a Virtual Machine Using Hyper-V, a Step-By-Step Guide
- Published: July 30, 2022
- Updated: August 2, 2022
Hyper-V is a virtual machine feature developed by Microsoft and first introduced in Windows Server 2008. With Hyper-V, you can create multiple virtual machines and run them on the same physical server.

With the Hyper-V platform, you can manage all running virtual machines from one panel, namely from the Hyper-V Manager.
Hyper-V is an integration of virtual servers on one piece of hardware, which significantly reduces the relevant costs. Moreover, Hyper-V allows for better use of hardware by allocating computing resources to those virtual machines that need them most. Thus, you can build an easily implemented virtual environment that will fully meet your needs and tasks.
Minimum Hyper-V System Requirements on a Windows Server
Before starting the Hyper-V installation process, make sure that your system meets the following requirements:
- 64-bit processor with second-level address translation (SLAT).
- Virtual Machine Monitor (this is a program that monitors the operation of several virtual machines in the system).
- Minimum 4 GB of RAM.
- Hardware virtualization (Intel VT or AMD-V).
- Hardware-based data execution prevention with NX bit for AMD systems or XD bit for Intel systems.

Installing Hyper-V
Hyper-V is a built-in option in Windows Server 2008 and later. However, it is not active by default, so you need to configure it manually. There are three ways to enable Hyper-V in Windows:
- Windows system settings.
- PowerShell Command-Line Interface (CLI).
- Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM).

Installation Process of Hyper-V using the Windows Control Panel
Let’s take a look at the most popular method and install Hyper-V using the Windows Control Panel:
1. In the search bar on the Taskbar, type “Settings” and press Enter.
2. After you have opened Settings, select Apps. Next, in the Related Settings section, click Programs and Features on the right-hand side.
3. On the left, select Turn Windows Features on or off.
4. In the Windows Features dialog box, select Hyper-V and click Ok.
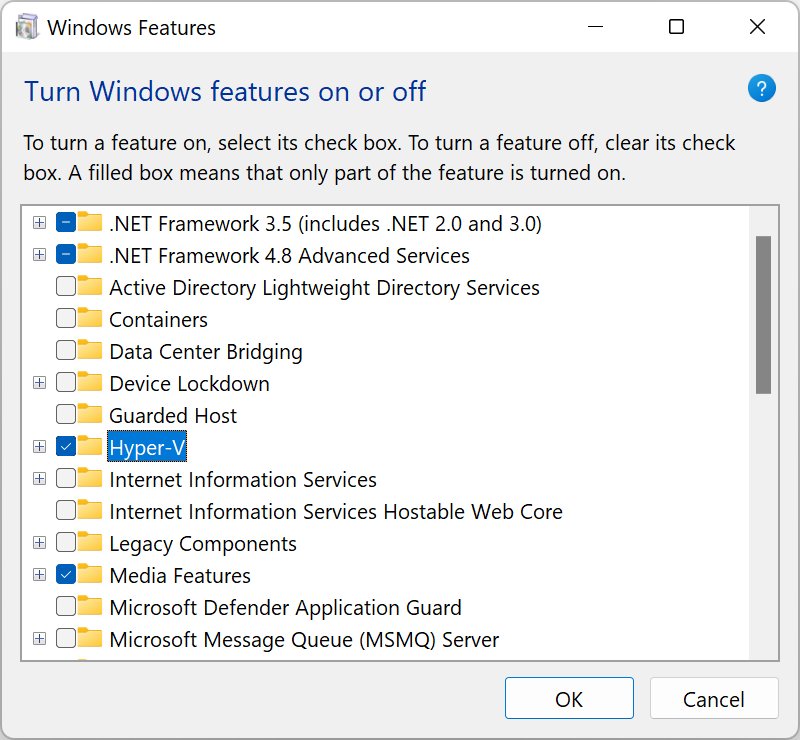
After completing the Hyper-V installation process, restart your computer to apply all the necessary changes.
Using Hyper-V Manager
To use Hyper-V on a full scale, you need to run the Hyper-V Manager application. You will find it in the list of installed programs.
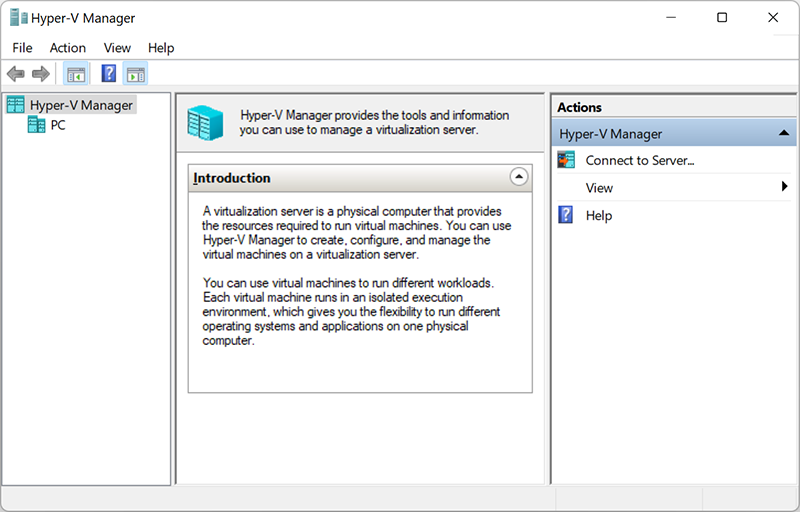
Hyper-V Manager is a server tool of its kind. It can be used to run virtual machines on your PC — in this case, your local computer works as a local virtualization server.
Creating a Virtual Switch for Hyper-V Virtual Machines
After installing Hyper-V on your computer, you can already start creating new virtual machines. But before doing that, you should think about creating a virtual switch, which in the future will be used to provide communication between virtual machines.
Moreover, it will allow you to connect virtual machines to both physical and virtual networks. Also, virtual switches enable transferring virtual machines from one physical host to another.
You can easily create a virtual switch using Hyper-V Manager by sticking to this step-by-step guide:
1. Open the Hyper-V Manager and select the host computer name.
2. In the Hyper-V Manager’s Quick Access toolbar, click Action and select Virtual Switch Manager from the drop-down menu.
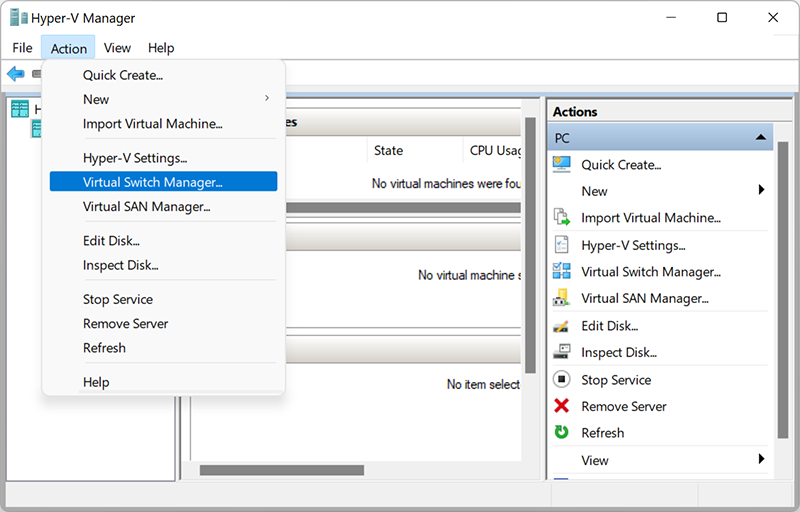
After Virtual Switch Manager opens, you should choose the type of three possible virtual switch:
- Internal Virtual Switch helps to create a virtual switch that is accessible only to virtual machines running on this physical computer, but does not provide access to a physical network connection.
- External Virtual Switch helps to create a virtual switch that provides virtual machines with access to a physical network by binding to a physical network adapter.
- Private Virtual Switch helps to create a virtual switch that can be used by virtual machines running on only one physical computer. Witch a private network, you can create an isolated network environment for which the outside access is not possible.
3. Select Create a Virtual Switch.
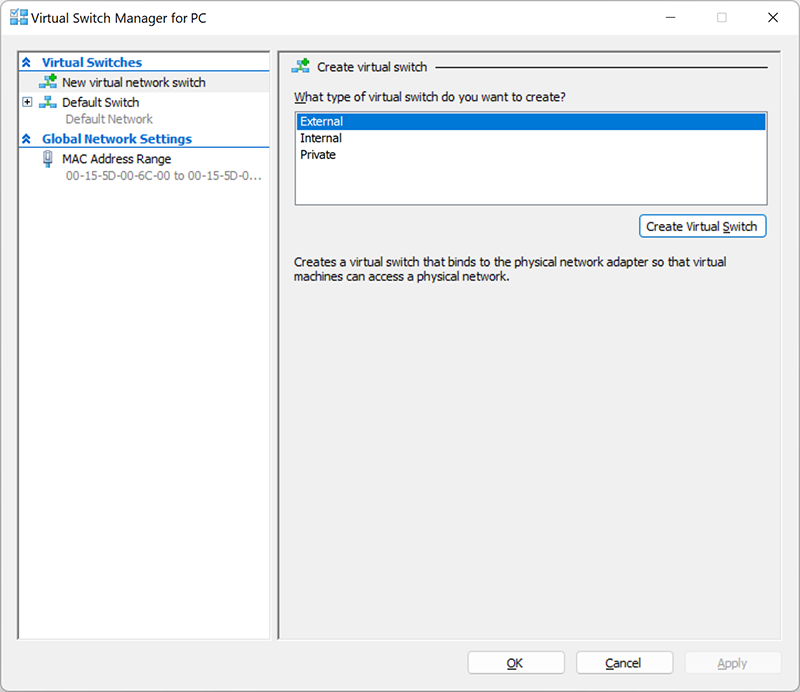
4. Next, give the virtual switch a name and click OK. The default settings are suitable in most cases, but we recommend you make sure that the connection to the external network is working. Be sure to choose a network adapter that is actually connected to the Internet, be it a Wi-Fi or wired connection.
5. Configure the connection type by selecting the Type of network to which the virtual switch is supposed to connect (external, internal, private). If it is an “External Network type”, you should select the type of network adapter that you want to use, and then check the “Allow the operating system to provide access to this network adapter” box.
Hyper-V supports VLAN operation (IEEE 802.1Q). You can manually configure this ID, which will then be used for network connections. For this end, in the properties of the virtual network interfaces, check the “Allow virtual LAN identification for the controlling operating system” box (or Enable VLAN Identification). This option is available for External and Internal network types.
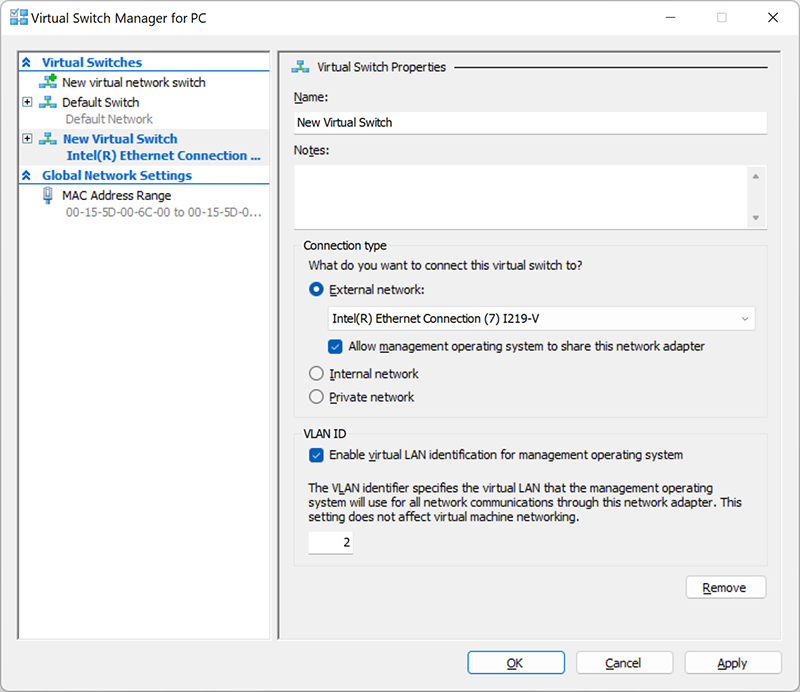
6. After you click OK, the following dialog box will appear:
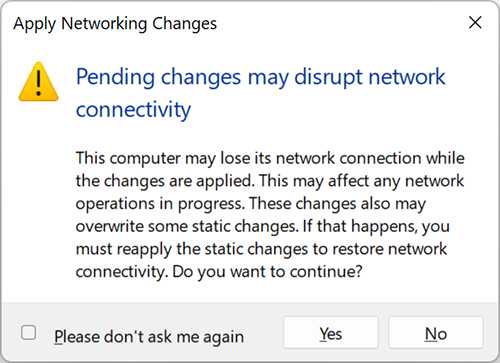
7. After you click Yes, a virtual switch will be created. Now your virtual environment can use its own virtual network to simplify the organization of multiple virtual machines.
Creating a Hyper-V Virtual Machine
Let’s look at the three main ways to create a Hyper-V virtual machine, which are carried out using:
- Hyper-V Manager
- PowerShell
- Hyper-V Quick Create

How to create a Hyper-V Virtual Machine using Hyper-V Manager
This is a fairly simple and intuitive method of creating a virtual machine. Let’s analyze it step by step:
1. In the search box on the Taskbar, type “Hyper-V Manager”. Open it by simply pressing Enter.
2. From the top of the quick access toolbar, find the Action menu and click Create in the pop-up window. And then select Virtual Machine.
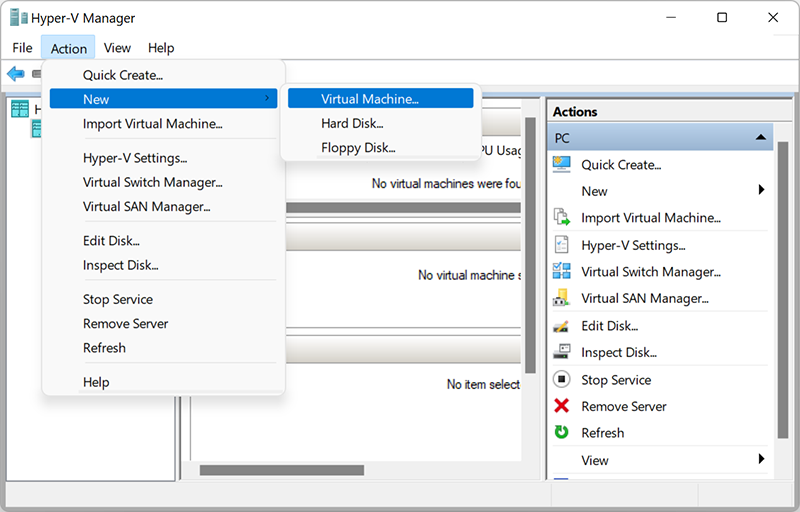
3. Next, the New Virtual Machine Wizard opens with a set of parameters, each of which you need to configure. Let’s take a closer look at each of them.
Configuring parameters when creating a Hyper-V Virtual Machine
Getting started
This section provides a brief overview of the Virtual Machine Wizard’s features and how to use it. We recommend reading it. You can also check the “Don’t show this page anymore” box if this information has been read or is not needed.
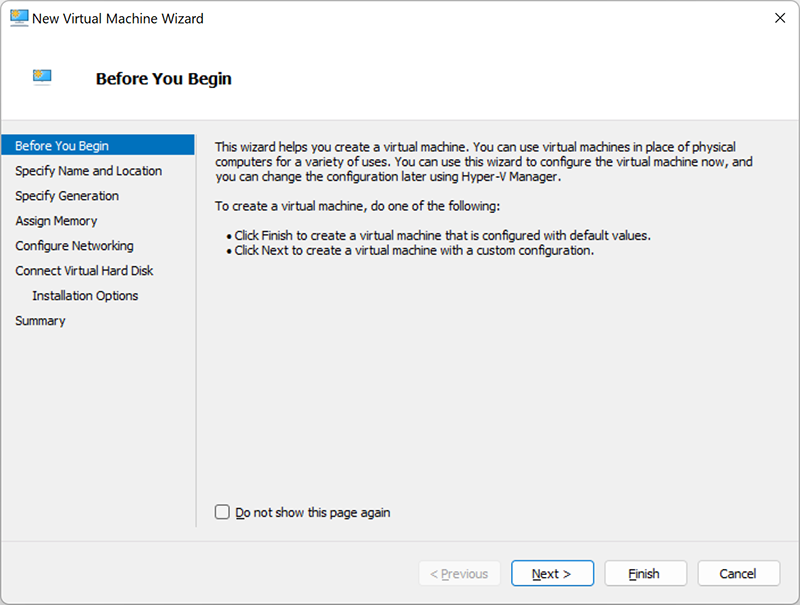
Enter the name and location
Here you can configure the name and location of the virtual machine. Make sure that this name is unique and easy to identify the Virtual Machine in the future. As for the location, you can either leave this default value, or create a folder and specify a path to it.
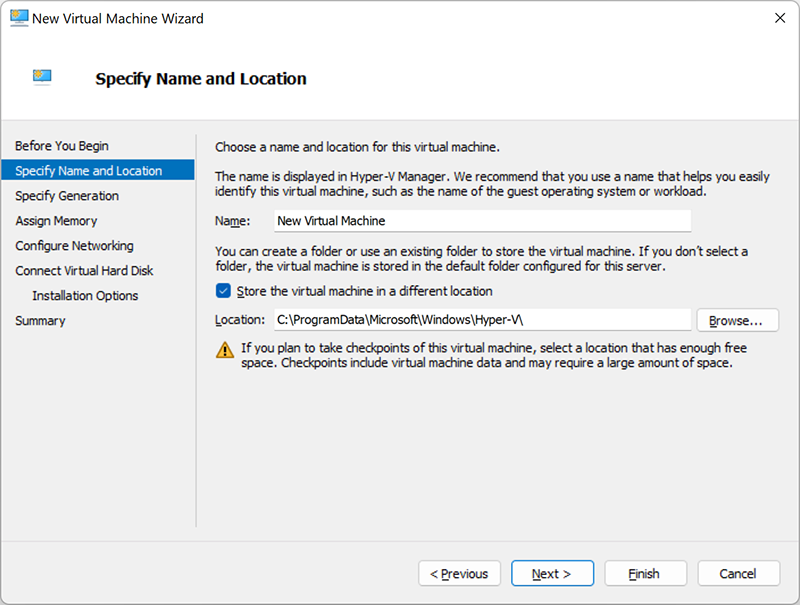
Specify the generation
The choice between generation 1 and generation 2 mainly depends on the guest operating system you want to install. Generation 1 virtual machines support 32-bit and 64-bit guest OS and BIOS-based architecture. Plus, they guarantee the functionality of earlier versions of Hyper-V. Generation 2 virtual machines support 64-bit Windows OS and the latest Linux and FreeBSD OS and also provide advanced virtualization features such as secure boot. When choosing, it is important to factor in all aspects, since you cannot change the generation of a virtual machine after its creation.
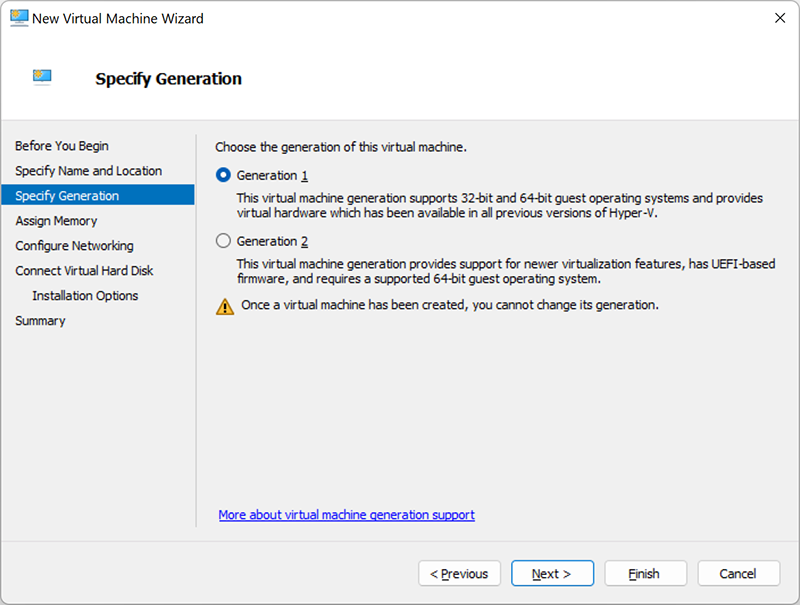
Allocate memory
Here you need to specify the memory (from 32 MB to 12,582,912 MB) that will be allocated for the virtual machine operation. Because its future performance will depend on it. In addition, you can choose dynamic memory by checking the box below. With this feature, you can take some of the memory that is available on the physical host and allocate resources to the virtual machine that needs them most.
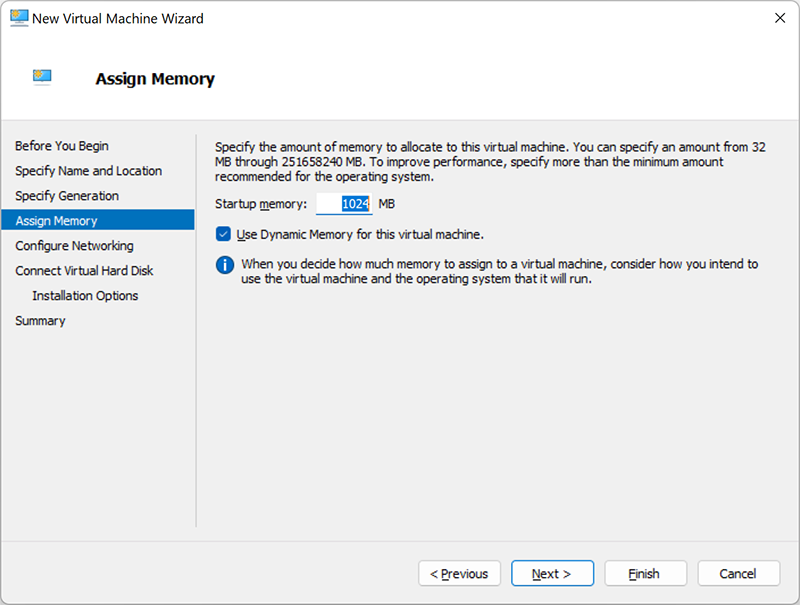
Network configuration
In this section, you need to select the virtual network that will be used to connect the virtual machine to the network. For this end, select the virtual switch that you created earlier. If you don’t have it, then there is only one option available – “Not Connected”. This means that your virtual machine has no network access.
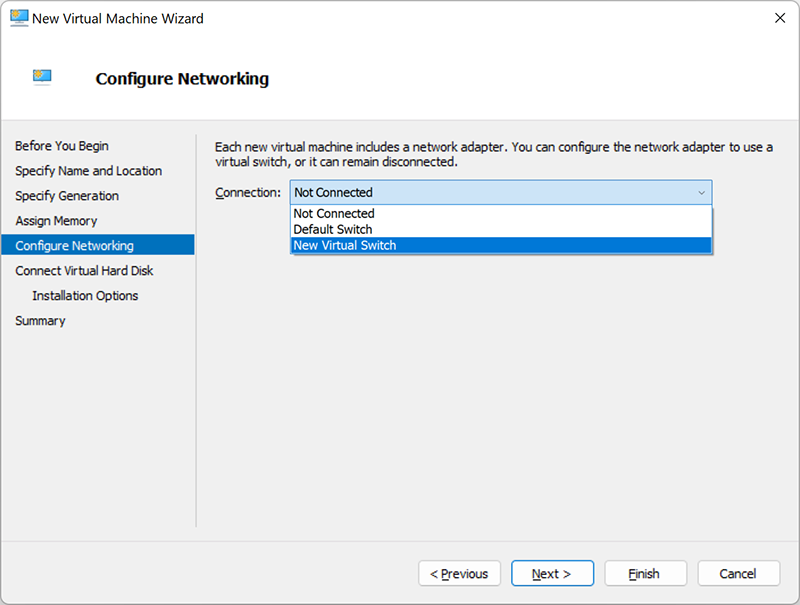
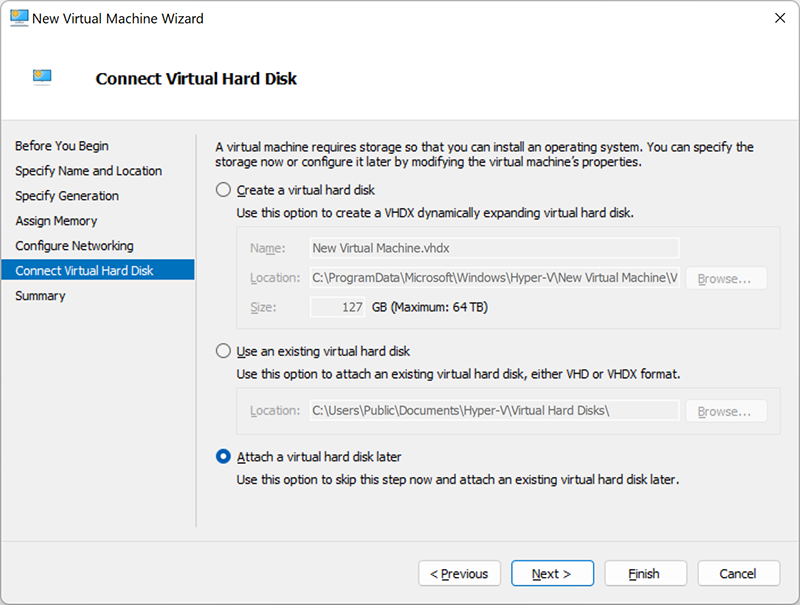
Connect a virtual hard disk
Here you can create a new virtual hard disk by specifying its name, location and size. It is also possible to use an existing disk (VHD or VHDX format). Or you can postpone this step for later.
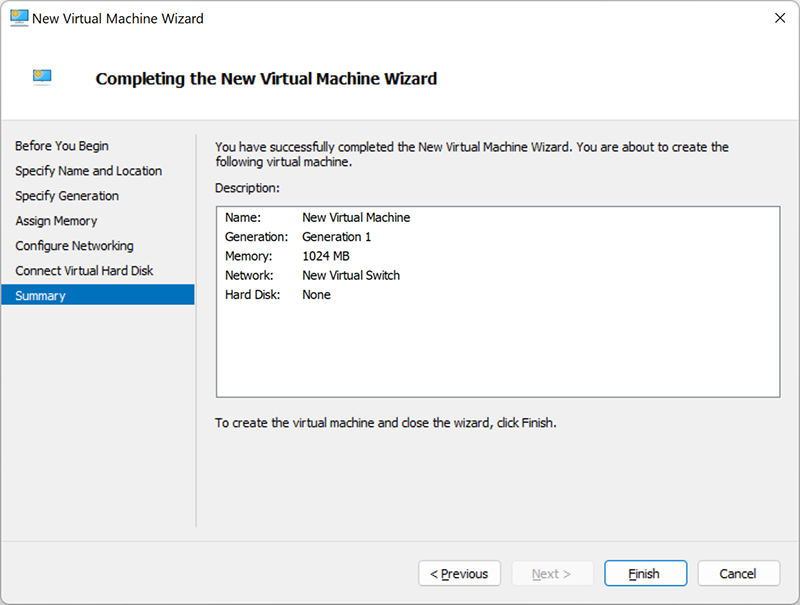
Summary
The last section contains a brief description of the virtual machine that you created. Check and, if everything is correct, click Finish.
How to Create a Hyper-V Virtual Machine Using PowerShell
If you want to create a full-scale virtual environment with several virtual machines running at the same time, this method is suitable for you. PowerShell allows for creation of various scripts that can be used to automate daily work tasks.
Let’s take a step-by-step dive into creation of a new Hyper-V Virtual Machine using PowerShell:
1. Type “Windows PowerShell” in the search bar.
2. Right-click on it and select Run as administrator.
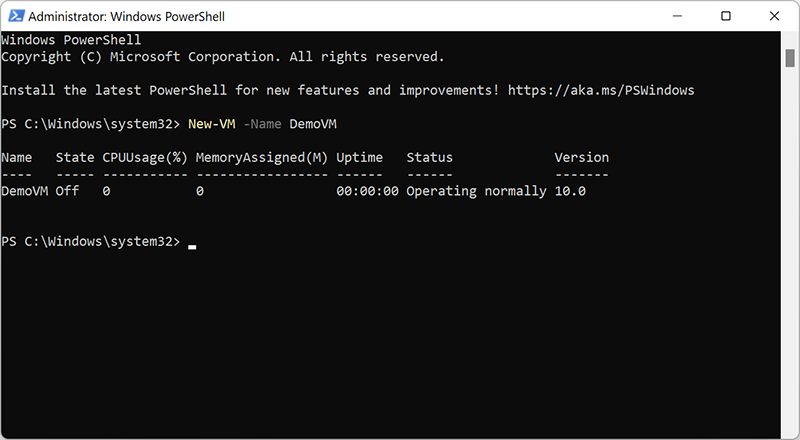
3. Write the following script (for a visual example, let’s call our new virtual machine “DemoVM”): New-VM -Name DemoVM
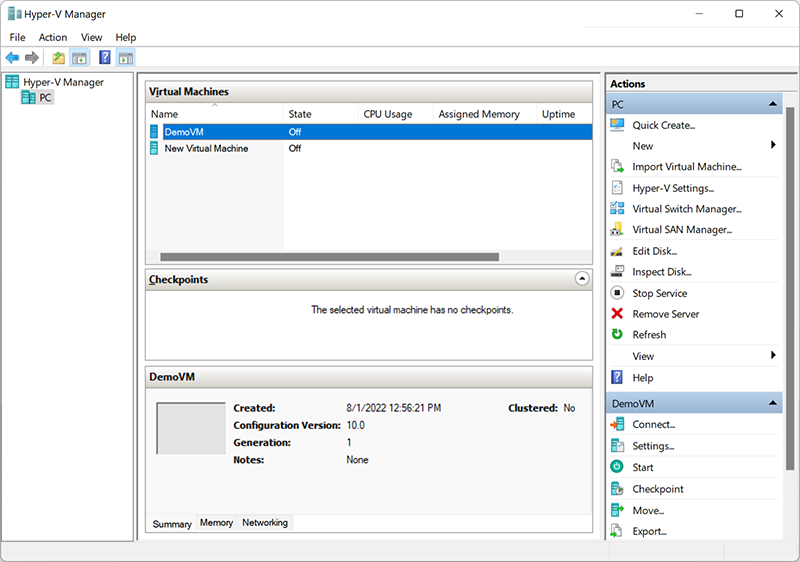
Check in the Hyper-V manager whether the Virtual Machine was created correctly. It should be in the off state, as this will allow you to presume its configuration process.
Creating virtual machines using PowerShell may seem tricky, but it’s actually a pretty simple process. The advantage of this method is that the PowerShell script can be extended, including additional configuration settings.
How to Create a Hyper-V Virtual Machine Using Hyper-V Quick Create
This method is unique; it can be performed in just a few clicks. Let’s try it together:
1. Open Hyper-V Quick Create
2. Select the operating system or install the guest OS from the ISO image file (.iso) or VHD file (.vhd or .vhdx) using a Local installation source. Click Change Installation source and select the desired file. The “Secure Boot” option can be selected only if the virtual machine supports Windows OS.
3. Click More options in the lower right corner. Next, enter the Name of the Virtual machine and the Virtual Switch.
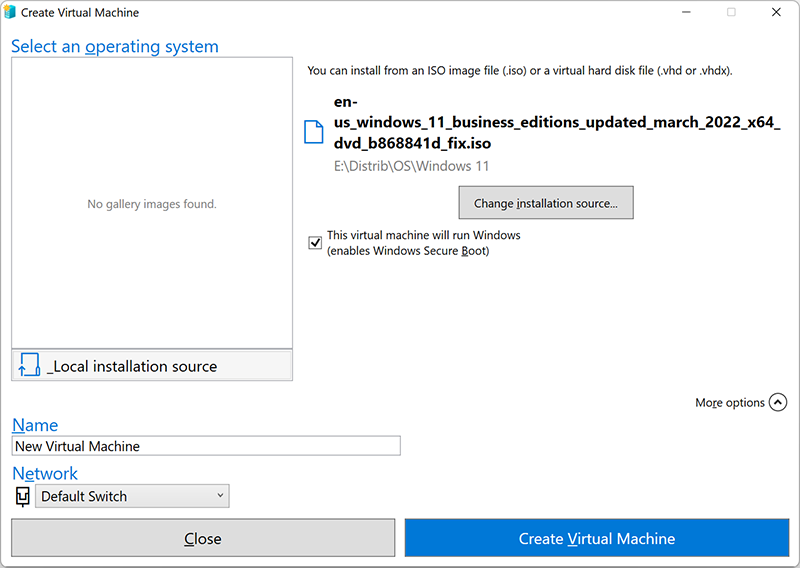
4. Click Create a Virtual Machine to start the process.
Running a Hyper-V Virtual Machine
After you have created a virtual machine, you can safely run it.
For this end, open the Hyper-V Manager, right-click on the virtual machine you want to start, and select Connect. After that, the VMConnect tool will be launched.
Even if your virtual machine is in a shutdown state, it will be automatically loaded when you click the Start button.
Hyper-V Security and Data Protection Guidelines
Hyper-V provides a virtualization platform on which you can create virtual environments of various scales and complexity. This greatly expands the user’s capabilities. But after creating a Hyper-V virtual machine, you need to prioritize its security and the safety of all files. There are various user and software data protection solutions for Hyper-V environments. We strongly recommend that you study the issue of backup, image-based replication, etc.
How to Restore Data on a Hyper-V VM
One of the main disadvantages of virtualization is that no system involves any built-in recovery functions. During operation, the user may encounter an operating system malfunction, virus attacks, inoperable virtual machine, or file system corruption. There can be many reasons for data loss.
In such situations, it is best to use specialized data recovery software. And the sooner you start, the more likely the successful extract of all the lost files is.
How to restore a virtual machine in Hyper-V using Magic Partition Recovery
To restore a deleted virtual machine, you need to restore the configuration and disk files of this virtual machine. Then, using the Virtual Machine Import function, import the recovered files into Hyper-V.
Let’s look at how to do this step by step using the example of the Magic Partition Recovery tool:
1. Download and install Magic Partition Recovery on your computer.
2. Run the program and scan the disk where the virtual machine files were stored.
3. In the program window, go to the storage folders of disk files, settings, and configuration of the virtual machine and restore them. It is important to remember that:
- *.vhdx is the disk file of the virtual machine. Default location: C:\Users\Public\Documents\Hyper-V\Virtual hard disks
- *.vmcx is a settings file of virtual machine configuration. Default location: C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Hyper-V\Virtual Machines
Successful recovery of these files will let you return a fully operational virtual machine with all the data on the disk.

How to Restore Files on a Hyper-V Virtual Machine Disk Using Magic Partition Recovery
In case of data loss on the virtual machine disk, you can also use the Magic Partition Recovery program. The tool includes the function of mounting virtual disks. Thanks to this function, you can easily restore all deleted files.
The key aspect for the successful operation of Magic Partition Recovery is that the program must be installed on the main Windows operating system, and not on the guest OS.
Let’s take a look at the basic steps to recover files from a Hyper-V disk:
1. Run the Magic Partition Recovery program and click Mount disk.
2. In the pop-up window, select Hyper-V and click Next.
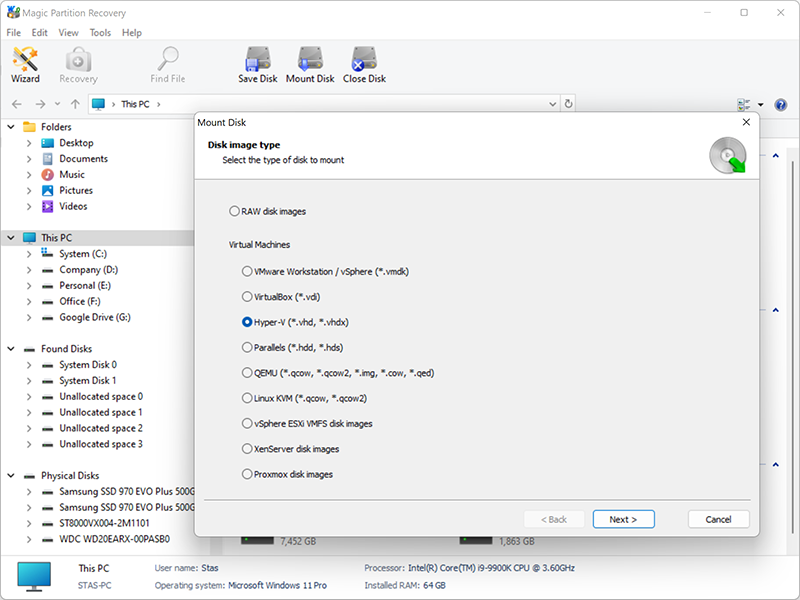
3. Next, go to the folder with the virtual machine and click OK.
4. After all the actions performed, the Mounted disk will be displayed in the program window. If you have multiple virtual machine disks, you can also mount them. After that, a complete list of all mounted disks will be displayed in the program window.
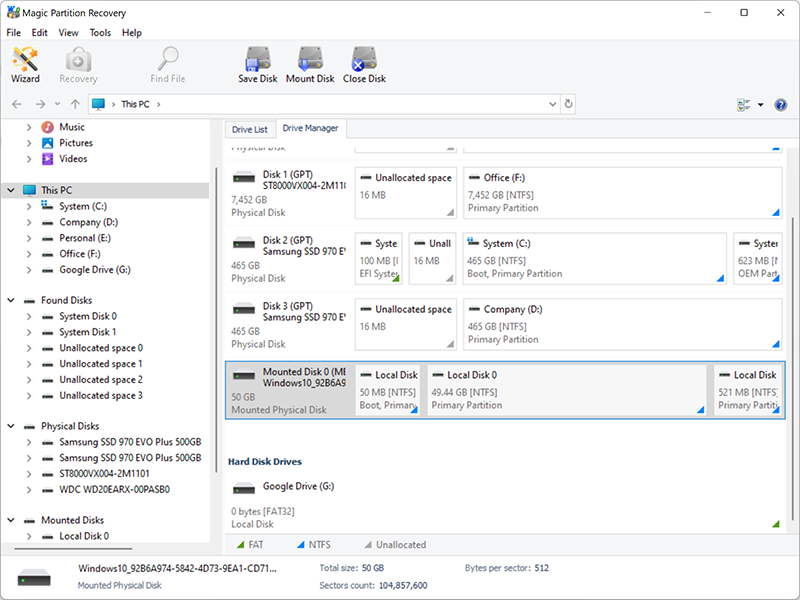
5. Click on the mounted disk and perform a scan.
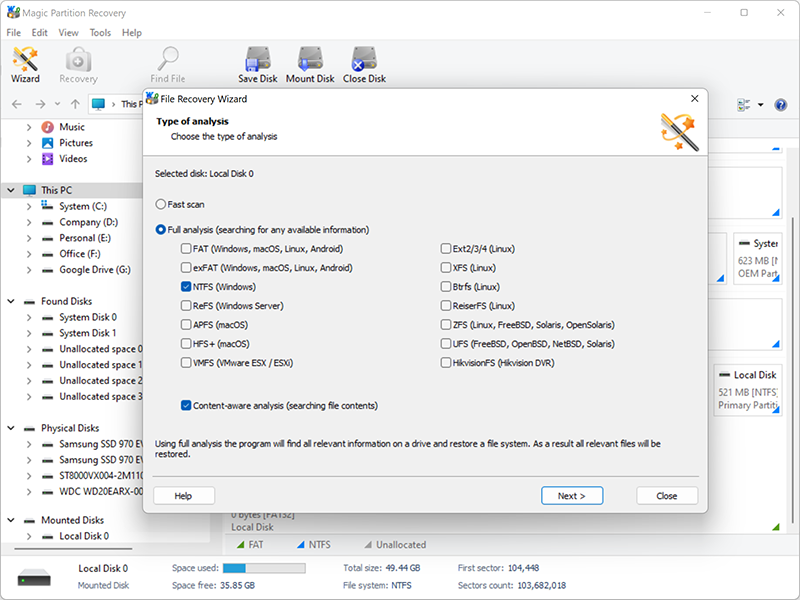
6. After the analysis is completed, the program will display all the files found. Find the necessary ones in the list and restore them.
Like This Article?
FAQ
-
Hyper-V allows you to run multiple operating systems as virtual machines in Windows. Each virtual machine acts as a complete computer running the operating system and programs.
-
*.vhdx is the disk file of the virtual machine. Default location: C:\Users\Public\Documents\Hyper-V\Virtual hard disks
*.vmcx is a settings file of virtual machine configuration. Default location: C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Hyper-V\Virtual Machines
-
You can use the software to extract all deleted data from Hyper-V. For example, the Magic Partition Recovery tool has a built-in function for recovering data from virtual machine disks. By the way, Magic Partition Recovery provides the ability to recover not only from Hyper-V disks, but also from almost all virtual machines that exist today, including the most popular ones, such as VMWare, Oracle VirtualBox, Linux-KVM, etc.
Stay Tuned






Comments